TradFi Stocks Explained: How Stock Markets Operate in Traditional Finance
In TradFi (Traditional Finance), stocks (also known as equities) are ownership securities that represent a shareholder’s claim on a company’s assets and earnings. Stocks are issued by companies and traded on regulated stock exchanges, forming the core of traditional equity markets.
By purchasing shares, investors become partial owners of a company and may receive shareholder rights such as dividends, voting rights, and residual claims in the event of liquidation. Unlike debt instruments, stocks do not provide fixed returns; their value fluctuates based on company performance, market expectations, and broader economic conditions.
Traditional stock markets operate at global scale, covering tens of thousands of listed companies and trillions of dollars in daily trading volume. They play a central role in capital formation and allocation, allowing companies to raise long-term funding while enabling investors to participate in economic growth through equity ownership.
This article explains how TradFi stock markets operate, including primary and secondary market processes, price discovery and order matching, key market participants, regulatory frameworks, risks, and how crypto platforms are expanding access to stock market exposure.
What Are Stocks in Traditional Finance?
For beginner investors, understanding how TradFi stock markets operate is a critical first step toward effective long-term portfolio construction. In the Traditional Finance (TradFi) system, stocks (also known as equities) are core financial instruments that represent ownership in a company. By purchasing shares, investors become shareholders and are legally entitled to shareholder rights, including dividend payments, voting rights, and claims on remaining assets in the event of liquidation.
From an asset classification perspective, stocks are equity assets. Unlike debt investments, stocks do not guarantee fixed returns. Their value depends on a company’s operating performance, profitability, and market expectations of future growth. As a result, stock prices are continuously influenced by company fundamentals, macroeconomic conditions, and investor sentiment.
Within TradFi stock markets, stocks are not only a key financing tool for companies, but also a central mechanism for capital allocation. Companies raise long-term capital by issuing shares, while investors participate in corporate growth and share in economic expansion through stock ownership. This mechanism forms the foundation of modern capital markets, making stock investing an indispensable part of the traditional financial system. This ownership-based structure distinguishes stocks from debt instruments and anchors their role within equity markets in traditional finance.
How Traditional Stock Markets Operate

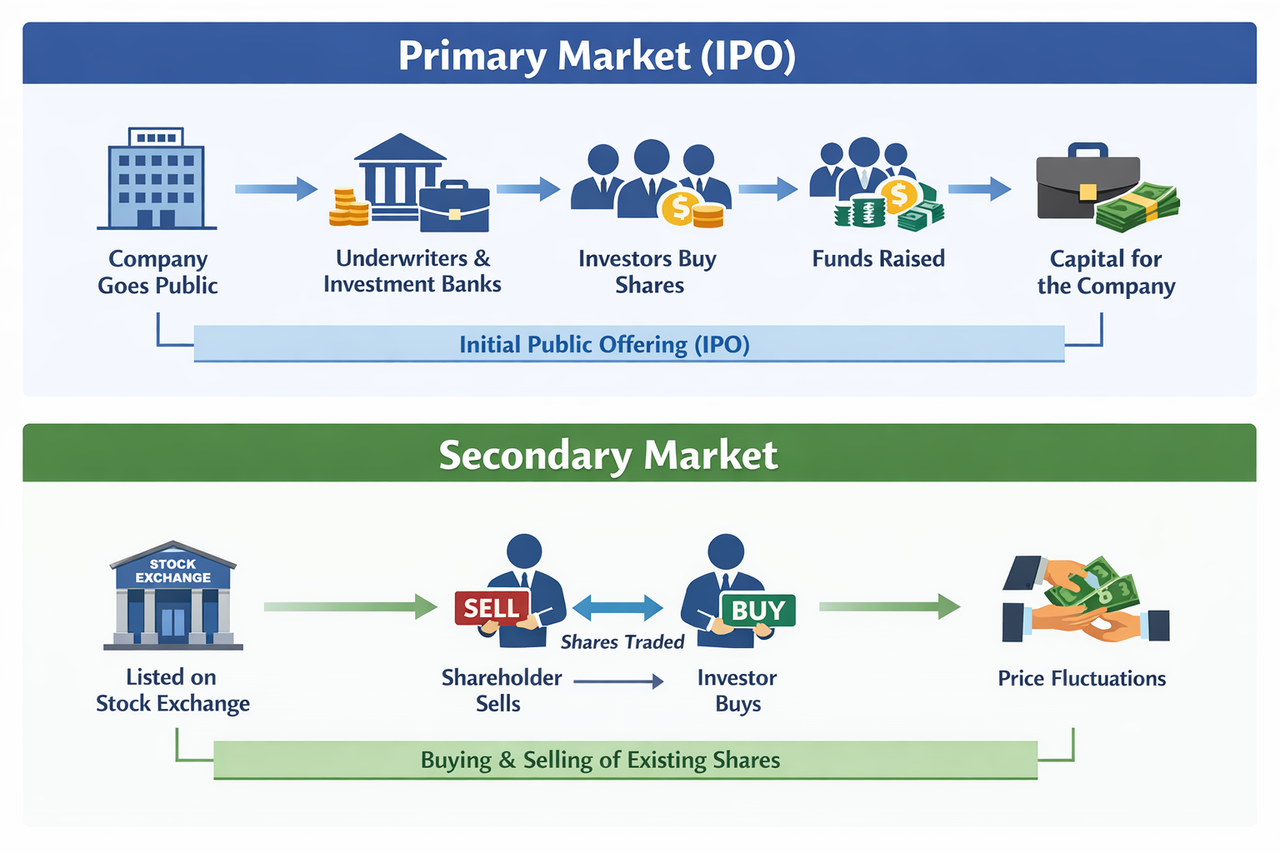
In TradFi stock markets, the primary market is responsible for stock issuance and corporate financing. When a company decides to go public, it typically issues new shares through an Initial Public Offering (IPO). Investors subscribe to shares in the primary market, and the funds raised flow directly to the company for business expansion, debt repayment, or research and development. The offering price is usually determined jointly by the company, investment banks, and underwriters after evaluating company fundamentals and market conditions.
The secondary market is where issued shares are traded among investors. Once stocks are listed on an exchange, investors can freely buy and sell them, with funds transferring between investors rather than to the company itself. The core function of the secondary market is to provide market liquidity and enable price discovery, allowing investors to adjust positions based on market information.
Together, primary and secondary markets ensure that TradFi stocks remain liquid, continuously priced, and accessible to global investors. In summary, the primary market addresses corporate financing needs, while the secondary market enables asset circulation. Together, they form a complete and efficient operating system for traditional stock markets, supporting both investor trading and corporate capital access.
Price Discovery and Order Matching in Stock Markets
In TradFi stock markets, trading is primarily executed through an order matching system. Investors submit buy or sell orders to exchanges, and the matching engine automatically pairs orders based on price priority and time priority.
Common order types include market orders and limit orders. Market orders are executed immediately at the best available price, prioritizing speed. Limit orders are executed only when the market reaches a specified price, prioritizing price control. This order framework improves trading efficiency while giving investors flexible tools for risk management and strategy execution.
Price discovery is one of the core functions of stock markets. Stock prices are not set by any single institution. Instead, they are formed dynamically through continuous interaction between buy and sell orders. Changes in company fundamentals, financial disclosures, macroeconomic data, and unexpected events are rapidly reflected in trading behavior, making stock prices a real-time expression of market information.
Key Participants in Traditional Stock Markets
TradFi stock markets consist of multiple participant groups that together form a complete and efficient ecosystem. Listed companies are the issuers, raising capital through stock offerings to support growth. Investors include both retail and institutional participants, such as mutual funds, insurance companies, pension funds, and hedge funds, all seeking returns through equity investments.
From a structural perspective, stock exchanges are the core infrastructure. Examples include the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ, which provide platforms for listing and trading shares. In addition, brokers, market makers, and clearing institutions play essential roles by executing trades, providing liquidity, and handling settlement of funds and securities.
Regulatory authorities are also a critical component of TradFi stock markets. They establish market rules, oversee trading activity, and ensure fairness and transparency. Cooperation across these participants and structures supports stable market operations and provides investors with a reliable trading environment.
Regulation, Risks, and Structural Limitations of Stock Markets
TradFi stock markets operate under strict regulatory oversight. Regulators require listed companies to disclose financial information regularly and enforce rules against insider trading and market manipulation. These measures protect investors and uphold market integrity. Understanding these constraints is essential when evaluating stock market risk in traditional finance systems.
Despite this, traditional stock markets still involve various risks and limitations. Market prices can deviate from company fundamentals due to investor sentiment, and information asymmetry cannot be fully eliminated. Retail investors often face disadvantages in expertise and information access compared to institutional participants.
In addition, limited trading hours, high barriers to cross-border investment, and relatively high intermediary costs are long-standing structural issues in TradFi stock markets. These characteristics highlight the importance of aligning investments with individual risk tolerance and using diversified strategies.
Stocks vs Bonds vs ETFs: Key Differences for Investors
In TradFi investing, stocks, bonds, and ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) are the most common financial instruments, but they differ significantly in risk-return profiles and investment strategies.
Stocks (or equities) represent ownership in a company and offer higher potential returns, but also higher volatility. They are suitable for investors seeking capital appreciation and able to tolerate market fluctuations. Bonds are debt instruments that provide fixed interest income and generally involve lower risk, making them suitable for conservative investors and portfolio risk diversification.
ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds) typically track an index or asset basket, offering diversification and liquidity. They allow investors to gain exposure to multiple assets through a single product, reducing single-security risk. Understanding these differences helps investors build portfolios aligned with their goals and risk tolerance.
How Crypto Platforms Enable Access to Stock Markets
As crypto assets increasingly integrate with Traditional Finance, some crypto platforms now offer convenient pathways into stock markets.
Gate TradFi, for example, offers products such as Stock Coins that allow users to trade stock-linked instruments using USDT and other crypto assets through tokenized or contract-based structures. Compared with traditional brokerage accounts, this approach offers more flexible onboarding, trading hours, and capital usage, while supporting fractional trading and lowering per-trade investment thresholds.
It is important to note that tokenized stock products are not the same as directly holding underlying shares. While prices track the referenced stocks, they may not include full shareholder rights. Investors should carefully understand compliance frameworks, settlement mechanisms, and platform-related risks before participating.
Overall, Gate TradFi provides an innovative bridge for crypto users to access traditional stock markets. However, it is best suited for investors who clearly understand product structures and risks, and who view it as a complement rather than a replacement for traditional stock investing.
Final Thoughts
In summary, TradFi stock markets create a complete system for financing and asset circulation through primary and secondary markets, supported by order matching and price discovery mechanisms that ensure trading efficiency and transparency. Understanding the differences between stocks, bonds, and ETFs enables investors to allocate assets more effectively based on risk tolerance and investment objectives.
While regulatory frameworks and disclosure requirements protect investors, traditional stock markets still face limitations such as volatility, information asymmetry, restricted trading hours, and barriers to cross-border participation. As crypto assets converge with TradFi, platforms like Gate TradFi introduce tokenized stocks and Stock Coins, enabling USDT-based participation, fractional investment, and more flexible strategies.
As financial infrastructure evolves, TradFi stocks and tokenized stock instruments are increasingly viewed as complementary tools within diversified investment strategies.
Whether investing through traditional brokerage accounts or tokenized platforms, investors should fully understand product features, risks, and opportunities. By combining diversified asset allocation with long-term strategy discipline, investors can pursue stable capital growth while managing risk effectively.
Further Reading
Related Articles

Gold Price Forecast for the Next Five Years: 2026–2030 Trend Outlook and Investment Implications, Could It Reach $6,000?

Crypto Future Profit Calculator: How to Calculate Your Potential Gains

Bitcoin's Future & TradFi (3,3)

Crypto Futures Calculator: Easily Estimate Your Profits & Risks

What is Oasis Network (ROSE)?
