TradFi Derivatives Explained: Futures, Options, and Other Financial Instruments
TradFi derivatives are financial contracts whose value is derived from an underlying asset or reference, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, interest rates, or currencies. Rather than representing ownership, derivatives allow market participants to manage price exposure, hedge risk, and improve capital efficiency without directly holding the underlying assets.
In traditional finance, derivatives were originally developed as risk management tools. Corporations and financial institutions use them to hedge interest rate fluctuations, currency risk, and commodity price volatility. Over time, these contracts evolved into highly liquid markets that support price discovery and risk transfer across the global financial system.
Today, TradFi derivatives markets are deeply embedded in equity, bond, commodity, and foreign exchange markets. With trading volumes and open interest reaching tens of trillions of dollars, derivatives have become a core pillar of modern capital markets, supporting institutional portfolios, liquidity provision, and systemic risk management.
This article explains how TradFi derivatives work, focusing on futures, options, and other common instruments. It covers core contract structures, pricing mechanisms, margin and leverage systems, regulatory frameworks, and key risks, helping beginners build a clear and structured understanding of traditional derivatives markets.
What Are Derivatives in Traditional Finance?

TradFi derivatives are financial contracts whose value is derived from an underlying asset or financial indicator. The underlying reference may include equities, interest rates, foreign exchange, commodities, or even indicators such as credit risk or volatility. In TradFi, derivatives are designed to separate price exposure from asset ownership, allowing market participants to manage risk more efficiently.
The core function of these financial derivatives is not simply to predict market direction, but to enable risk management, price locking, and hedging. Originally, derivatives primarily served corporations and financial institutions as tools to hedge risks from exchange rates, interest rates, or commodity price fluctuations. As markets evolved, derivatives gradually developed into highly liquid trading markets, providing investors with flexible tools for risk transfer and capital efficiency. This risk-transfer function explains why derivatives are widely used in traditional finance as hedging tools rather than speculative instruments alone.
How Futures and Options Work
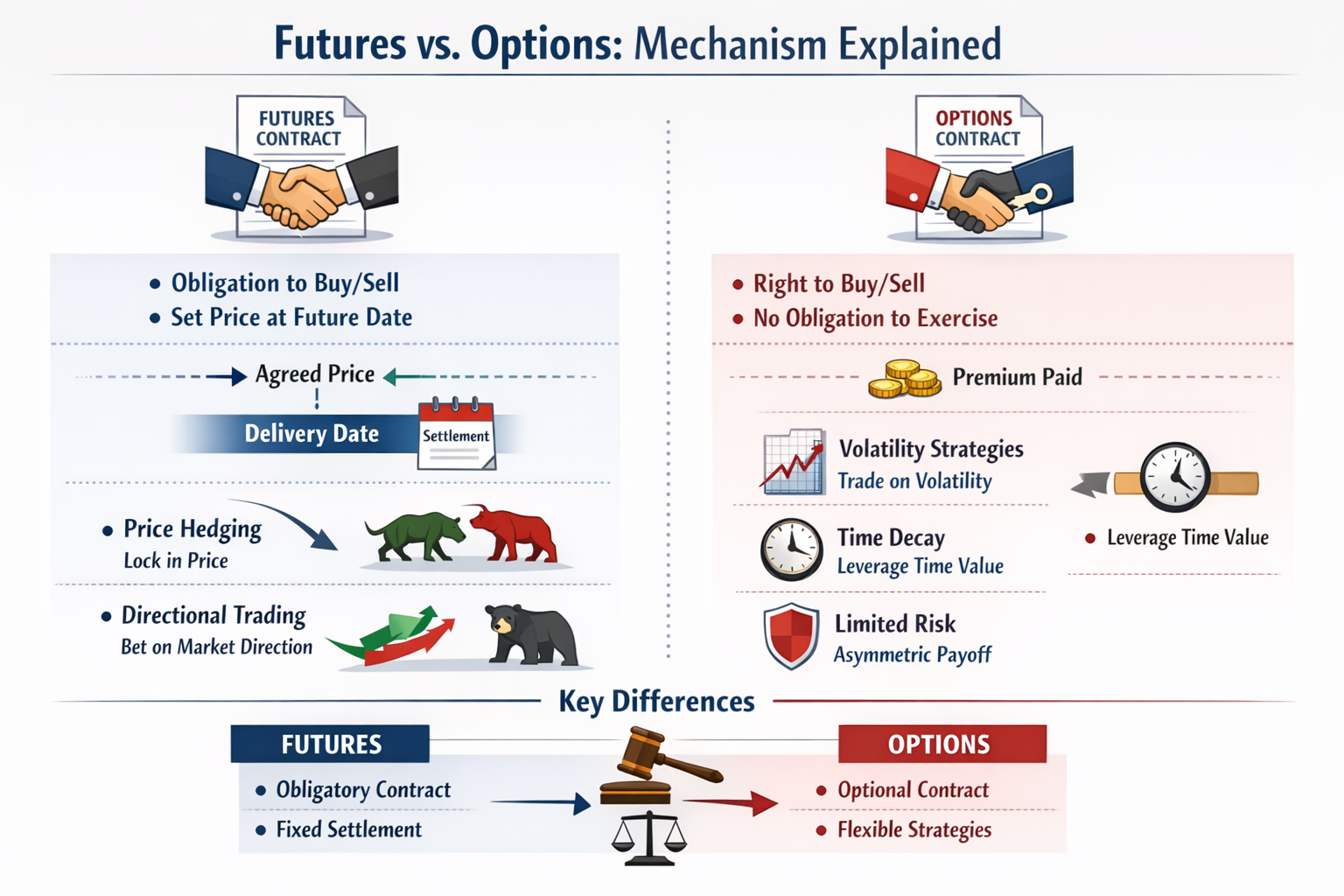
Within TradFi derivatives, futures contracts and options contracts are the two most representative instruments, yet they are often confused by investors. A futures contract is a bilateral obligation contract, requiring both parties to buy or sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price on a specified future date. An options contract, by contrast, is a rights-based contract, granting the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to execute the transaction. Understanding the structural difference between futures and options is fundamental to navigating TradFi derivatives markets effectively.
From a trading logic perspective, futures contracts emphasize price locking, directional exposure management, and hedging, while options contracts offer more flexible payoff structures. Options allow traders to design strategies based on volatility, time value, and asymmetric risk exposure.
Common Types of TradFi Derivatives
Within the TradFi derivatives system, instruments extend beyond futures and options to include swaps and forward contracts, forming a multi-layered market structure. Different derivative types serve investors of varying scales and risk profiles, each with distinct characteristics and trading logic:
- Futures: Standardized contracts traded on exchanges, offering high liquidity and suitable for price locking and risk management.
- Options: Asymmetric risk instruments that allow investors to flexibly deploy strategies based on volatility, time value, and structured combinations.
- Swaps: Primarily used for interest rate, foreign exchange, or credit risk management, typically traded over the counter (OTC), and suited for institutions or corporations managing long-term risk.
- Forwards: Highly customized contracts designed to meet specific transaction needs, with relatively lower liquidity and transparency, commonly used by corporations or financial institutions for risk locking.
Together, these core TradFi derivative types form the foundational framework of the traditional derivatives market, providing investors with flexible risk management tools and diversified strategic options.
Pricing, Margin, and Risk Management Mechanisms
In the TradFi derivatives market, pricing formation relies on mature margin systems and clearing mechanisms. Traders are not required to pay the full notional value of a contract; instead, they post margin to establish leveraged positions, making leverage an inherent feature of derivatives trading. Margin-based trading is a defining characteristic of how leverage operates within TradFi derivatives markets.
To reduce systemic risk, exchanges typically implement mark-to-market accounting, margin calls and forced liquidations, and risk reserve mechanisms. These systems ensure market stability and transaction safety even during periods of extreme volatility.
This margin and leverage structure significantly improves capital efficiency, allowing investors to control larger positions with relatively small amounts of capital. However, it also amplifies potential losses from incorrect decisions, forming the core reason why TradFi derivatives exhibit both high return potential and high risk.
How Derivatives Are Used for Trading and Hedging
In TradFi derivatives markets, financial institutions and corporations widely use derivatives for hedging, portfolio allocation, interest rate management, and cross-market arbitrage. These applications help reduce price volatility risk, optimize capital structures, and improve capital efficiency.
However, derivatives trading also carries inherent risks. Excessive leverage, complex derivative structures, and the opacity of OTC markets can amplify market volatility and trigger systemic risk. While derivatives themselves do not create risk, their high leverage and complexity allow risk to propagate more rapidly. This is a core reason why global regulatory authorities closely monitor and strictly regulate TradFi derivatives markets.
Regulatory Framework for TradFi Derivatives
The TradFi derivatives market operates under strict regulatory oversight. Different jurisdictions assign clear regulatory responsibilities. Exchange-traded derivatives are typically supervised by securities regulators or futures regulators, while OTC derivatives were progressively brought under central clearing and trade reporting requirements following the 2008 global financial crisis.
The primary objective of regulation is not to restrict derivatives trading, but to prevent the uncontrolled spread of systemic risk through transparency, risk management standards, and compliance requirements, ensuring the stability and capital efficiency of TradFi derivatives markets.
Risks and Considerations for Derivatives Investors
For investors, understanding risk is more important than pursuing returns. Key considerations include leverage risk, liquidity risk, and liquidation mechanisms under extreme market conditions. Insufficient understanding of contract terms and structures across futures, options, swaps, and forwards can also lead to unexpected losses.
Derivative trading emphasizes discipline, strategic planning, and strict risk management to reduce both systemic and individual risk and to support stable portfolio performance.
Accessing Derivative Markets via Crypto Platforms

As crypto markets develop, an increasing number of platforms have introduced traditional derivative logic into on-chain trading or centralized crypto exchange systems. Perpetual contracts, index contracts, and synthetic assets lower entry barriers, enable 24/7 trading, and improve settlement efficiency, allowing users to access derivatives markets at lower cost, though investment risks remain. This trend reflects a broader shift in which crypto platforms are replicating traditional derivatives market structures using digital infrastructure.
The key advantage of accessing derivatives through crypto platforms lies in using familiar crypto trading frameworks to directly participate in traditional financial price movements. For example, Gate TradFi offers trading models that allow users to trade derivatives linked to foreign exchange, stock indices, and commodities via contracts for difference, without opening traditional brokerage accounts.
Trading funds are denominated in USDT and automatically converted to USDx, while margin and profit-and-loss logic remains consistent with traditional derivatives markets. Combined with clear leverage rules and risk management systems, this allows crypto traders to enter traditional derivatives markets with low friction, focusing on strategy and price opportunities rather than institutional and procedural transitions.
Final Thoughts
TradFi derivatives provide investors with diverse tools for risk management, price discovery, and capital efficiency, while crypto platforms lower entry barriers and enable 24/7 trading with faster settlement. Whether futures, options, swaps, or forwards, understanding leverage, margin, and risk mechanisms remains essential for successful participation.
As derivatives trading evolves, the convergence of TradFi market logic and crypto-native execution is becoming increasingly relevant for global investors. With platforms such as Gate TradFi, investors can efficiently engage in derivatives markets within familiar crypto environments while maintaining strategic flexibility and controlled risk exposure.
Further Reading
Related Articles

Gold Price Forecast for the Next Five Years: 2026–2030 Trend Outlook and Investment Implications, Could It Reach $6,000?

Crypto Future Profit Calculator: How to Calculate Your Potential Gains

Bitcoin's Future & TradFi (3,3)

Crypto Futures Calculator: Easily Estimate Your Profits & Risks

What is Oasis Network (ROSE)?
